


Riddle: Peroxodisulfate and hydroxide
In this simple experiment, a solid peroxodisulfate is mixed with solid sodium hydroxide. This experiment works best with sodium peroxodisulfate, but it also works with potassium peroxodisulfate and ammonium peroxodisulfate.
Questions, raised during these experiments, are (1) what is the yellow compound, which is formed when a little water is added?
![]()
![]() Required
chemicals:
Required
chemicals:
- sodium peroxodisulfate, Na2S2O8
- (optional) potassium peroxodisulfate, K2S2O8
- sodium hydroxide
![]() Required
equipment:
Required
equipment:
- test tube
![]() Safety:
Safety:
- Sodium hydroxide is very corrosive, especially for the eyes. At any cost avoid contact with the eyes. If sodium hydroxide comes in contact with the skin then rinse with water, until the slippery feeling is gone.
- Sodium peroxodisulfate is a strong oxidizer and somewhat corrosive.
- The reaction between sodium hydroxide and sodium peroxodisulfate can be quite violent. Do not scale up the experiment with larger quantities.
![]() Disposal:
Disposal:
-
The chemicals, used in this experiment, can be flushed down the drain with a large amount of water.
![]()
Mixing the solid chemicals
Take a big spatula of sodium peroxodisulfate and put this in a dry test tube. It is important that the test tube is dry! Add a similar amount of solid sodium hydroxide to the sodium peroxodisulfate and swirl the test tube, such that both chemicals are mixed well. The result is a white mass.
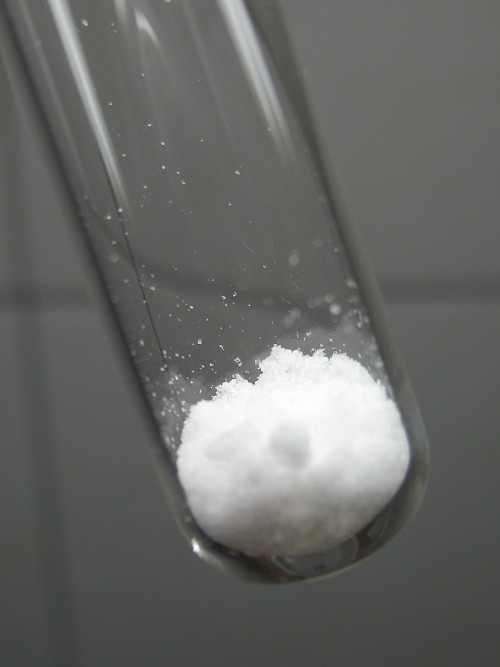

Adding a little amount of water: formation of yellow compound
To this solid mass add a single large drop of distilled water. Do not add too much water at once! When the water is added, then quickly, the sodium hydroxide becomes covered by a yellow layer:
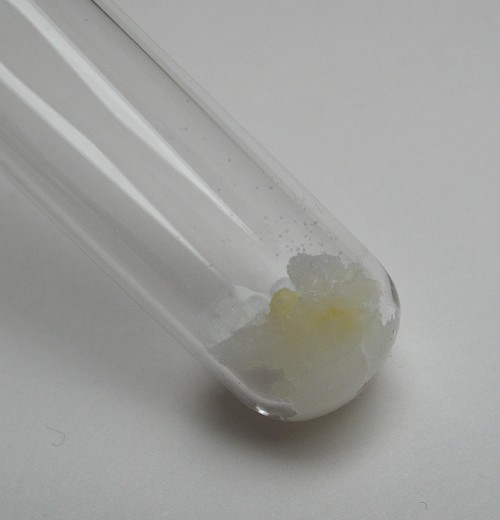

On standing, a gas is produced, and more of the yellow material is formed:
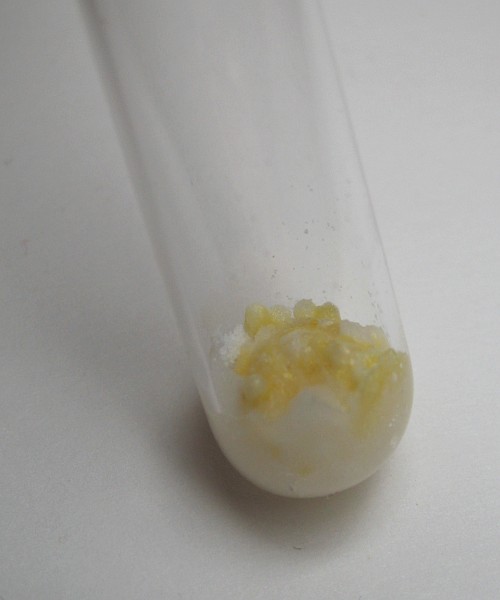

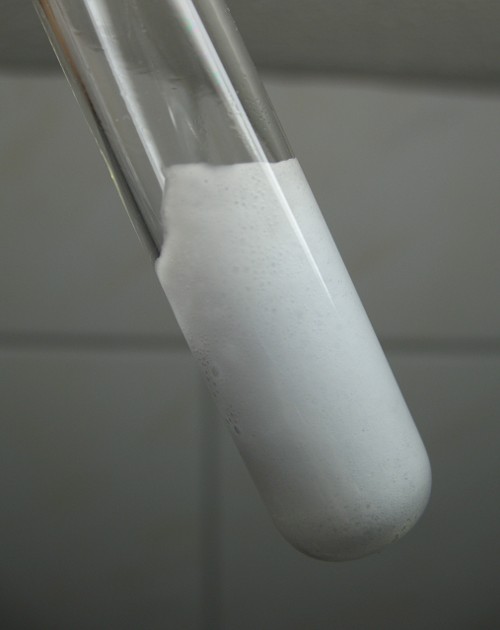
Adding a little more water: very violent reaction
When a little more water is added (just a few drops), then the reaction becomes much more violent and a lot of heat is produced. The contents of the test tube starts frothing and foaming:
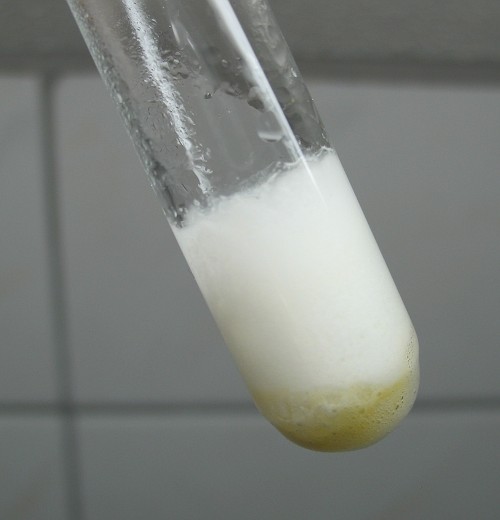
After a while, the yellow color has gone and the test tube is filled with a layer of white foam in which there is a lot of bubbles of gas. This foam is very hot.

![]()
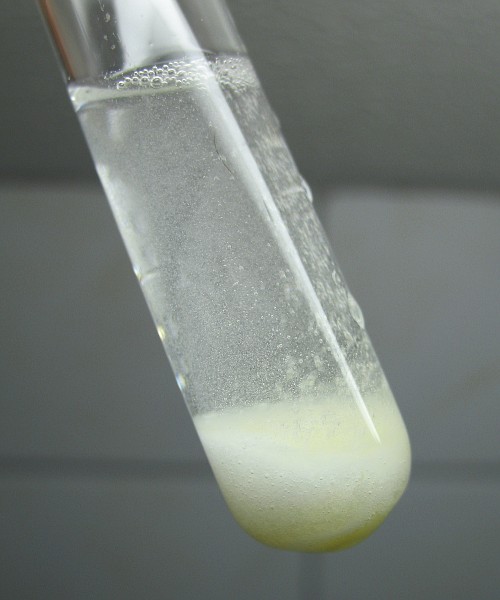
The experiment was repeated with potassium peroxodisulfate and sodium hydroxide. In this experiment, no visible yellow compound was formed when a little water was added to the mix of the two solids. Probably this is due to the much lower solubility of potassium peroxodisulfate in water. When a lot of water is added, then slowly a yellow compound is formed in the bottom of the test tube and gas is produced. There is no violent reaction in this case.

![]()
Discussion of the results
The appearance of a yellow compound when peroxodisulfate and hydroxide ions are mixed at high concentrations is quite remarkable. All starting ions are colorless. The yellow material seems to be soluble in water, and most likely is a solid when pure. It is very unstable though, it only exists for minutes and when diluted with water, then it quickly disappears.
So, the question is: What is the yellow compound, formed on mixing of hydroxide and peroxodisulfate at high concentration, in the presence of water?