

Sodium and potassium
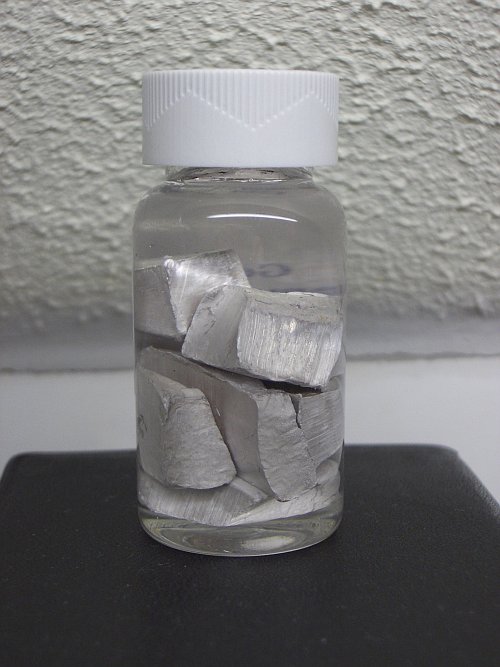 Sodium and potassium are the two most common alkali
metals. The picture shows a sample of sodium metal. Both metals are encountered in many compounds, both in the lab, but also in
everyday life. Sodium and potassium are essential to life, for humans, for
animals and for plants.
Sodium and potassium are the two most common alkali
metals. The picture shows a sample of sodium metal. Both metals are encountered in many compounds, both in the lab, but also in
everyday life. Sodium and potassium are essential to life, for humans, for
animals and for plants.
The elementary metals are silvery metals, which quickly tarnish in air. They react violently with water, potassium almost explosively. In the reaction with water, the metal hydroxide and hydrogen are produced. The reaction with potassium is so violent that the hydrogen is ignited. In the reaction with sodium this also can happen, but not always. In aqueous (and virtually all other) media, the metals only exist in the +1 oxidation state, as simple hydrated univalent ions. Sodium and potassium ions are extremely inert. For the home chemist it is almost impossible to have sodium or potassium ions take part in an interesting chemical reaction.
For the home lab, sodium and potassium metal are not really interesting. They are too reactive to be useful. These metals must be stored under a layer of mineral oil, which protects them from moisture and oxygen. Sometimes with some good luck, the metals are available through eBay. The sample of sodium, shown here, was obtained in this way.
![]()
Although sodium and potassium are constituents of many compounds, they seldom are the active part of the compound. The properties of the compounds, containing sodium or potassium, usually are determined by the anion. In many cases it does not really matter, whether one has the sodium salt or the potassium salt of a given anion. Sometimes, however, the sodium salt of a certain anion is preferred and at other times the potassium salt is preferred. Chemically speaking, the sodium and potassium salts of the same anion will be very similar, but there can be quite large differences in solubility and hygroscopic properties. Some examples:
- Potassium dichromate is not hygroscopic at all, while sodium dichromate is very hygroscopic. Solutions of sodium dichromate can be made very concentrated. Which one is preferred depends on what the salt is used for.
- Potassium nitrate is a free flowing powder, which remains dry on storage. Sodium nitrate is hydroscopic. Both solids dissolve well in water. This makes potassium nitrate more attractive for lab-purposes.
- Sodium thiosulfate is a stable crystalline solid, while the potassium salt is deliquescent and becomes wet easily. This makes storage of the potassium salt really difficult. The sodium salt can be stored without decomposition indefinitely.
From the viewpoint of the home chemist, sodium-ion, potassium-ion and ammonium-ion are comparable. Almost all interesting chemical compounds, which are interesting because of their anion-part are either sodium salts, potassium salts or ammonium salts. This is because the cation does not interfere with the properties of the anion in the compound's intended application.