

Calcium
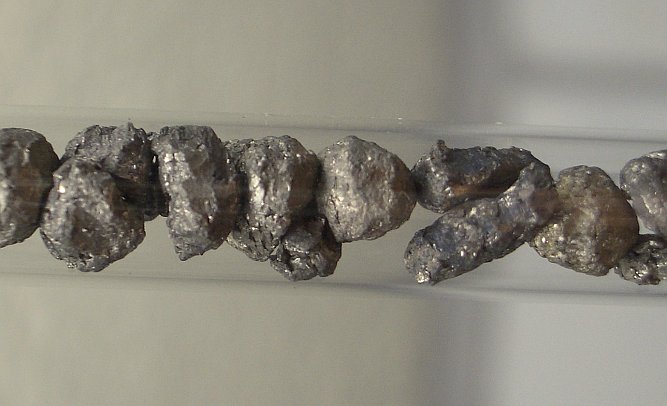 Calcium is a reactive silvery grey metal. It reacts with
water, forming hydrogen and calcium hydroxide. Calcium, however, is not as
reactive as its neighbor sodium. When calcium is put in water, then a continuous
flow of hydrogen is produced, but the reaction is not violent.
Calcium is a reactive silvery grey metal. It reacts with
water, forming hydrogen and calcium hydroxide. Calcium, however, is not as
reactive as its neighbor sodium. When calcium is put in water, then a continuous
flow of hydrogen is produced, but the reaction is not violent.
Calcium does not keep very well. It easily becomes oxidized, forming calcium oxide and with carbon dioxide from the air, this is easily converted to calcium carbonate.
For the home lab, elementary calcium is of limited interest. It sometimes can be purchased in small quantities on eBay for acceptable prices. When one has access to magnesium, then calcium does not add much new anymore.
![]()
Compounds of calcium always contain the element in the +2 oxidation state. Calcium forms ionic compounds, it hardly has any covalent character. The divalent Ca2+ ion is a colorless ion in aqueous solutions. Calcium compounds are white or transparent/colorless, at least when the anion has no color.
Calcium ions are not reactive. They have no redox chemistry in water and the coordination chemistry also is limited. Calcium forms precipitates with many anions. Examples are carbonate, sulfite, phosphate. These precipitates usually are white.
From the point of view of the home chemist, calcium compounds are not really interesting. Some compounds can, however, easily be obtained and can have some interesting applications.
- Calcium chloride, CaCl2
- Calcium carbide, CaC2
- Calcium carbonate, CaCO3
- Calcium phosphate, Ca3(PO4)2
- calcium hypochlorite, Ca(ClO)2
- Calcium oxide, CaO
- Calcium sulfate, CaSO4
![]() Calcium chloride is a white solid, which is very hygroscopic. It can absorb so
much water, such that it dissolves in the water it attracts. For this purposes,
technical grade calcium chloride is sold at hardware stores. Calcium chloride
can be interesting for storing moisture sensitive chemicals in an air-tight
enclosure, in which the chemical and the calcium chloride are stored in separate
smaller containers, with the calcium chloride container in open contact with the
air in the large container. One must keep in mind, that calcium chloride
liquefies, when it absorbs a lot of moisture. This may impose the risk of
spoiling the other chemical, if not stored or transported properly.
Calcium chloride is a white solid, which is very hygroscopic. It can absorb so
much water, such that it dissolves in the water it attracts. For this purposes,
technical grade calcium chloride is sold at hardware stores. Calcium chloride
can be interesting for storing moisture sensitive chemicals in an air-tight
enclosure, in which the chemical and the calcium chloride are stored in separate
smaller containers, with the calcium chloride container in open contact with the
air in the large container. One must keep in mind, that calcium chloride
liquefies, when it absorbs a lot of moisture. This may impose the risk of
spoiling the other chemical, if not stored or transported properly.
![]() Pure calcium carbide is a white solid. The grade, available to the general
public, called 'carbid' is a grey crystalline solid, which is sold in the form
of large lumps. This compound is not interesting because of the calcium it
contains, but because of the carbide ion, C22-. More info
on this can be found in the section about carbon.
Carbid is sold at smaller hardware shops and some fireworks sellers just before
the end of the year. It is used as a cheap, yet powerful, alternative for
fireworks by many people (at least in the Netherlands).
Pure calcium carbide is a white solid. The grade, available to the general
public, called 'carbid' is a grey crystalline solid, which is sold in the form
of large lumps. This compound is not interesting because of the calcium it
contains, but because of the carbide ion, C22-. More info
on this can be found in the section about carbon.
Carbid is sold at smaller hardware shops and some fireworks sellers just before
the end of the year. It is used as a cheap, yet powerful, alternative for
fireworks by many people (at least in the Netherlands).
![]() Calcium carbonate is a white solid, which hardly dissolves in water. As most
carbonates, it can easily be dissolved in dilute mineral acids. For the home
lab, this is not a very interesting chemical. In certain pyrotechnic mixtures,
it may be interesting. Calcium gives a reddish flame color when mixtures,
containing this metal are burned. Calcium carbonate can be obtained at many
drugstores.
Calcium carbonate is a white solid, which hardly dissolves in water. As most
carbonates, it can easily be dissolved in dilute mineral acids. For the home
lab, this is not a very interesting chemical. In certain pyrotechnic mixtures,
it may be interesting. Calcium gives a reddish flame color when mixtures,
containing this metal are burned. Calcium carbonate can be obtained at many
drugstores.
![]() Calcium phosphate is covered in the section about
phosphorus. It is not a really interesting chemical for the home lab.
Calcium phosphate is covered in the section about
phosphorus. It is not a really interesting chemical for the home lab.
![]() Calcium hypochlorite is an interesting chemical for the home lab. It is a strong
oxidizer, useful in many interesting experiments. Again, this is not due to the
calcium in the compound, but due to the anion. More info on this compound can be
found in the section about chlorine.
Calcium hypochlorite is an interesting chemical for the home lab. It is a strong
oxidizer, useful in many interesting experiments. Again, this is not due to the
calcium in the compound, but due to the anion. More info on this compound can be
found in the section about chlorine.
![]() Calcium oxide is a white powder, which reacts with water, producing a lot of
heat. The reaction product is calcium hydroxide. Calcium oxide is a very caustic
chemical and should be handled with care. As drying agent it is even better than
calcium chloride. While absorbing water, it does not liquefy. Impure calcium
oxide can be obtained as cement in hardware stores.
Calcium oxide is a white powder, which reacts with water, producing a lot of
heat. The reaction product is calcium hydroxide. Calcium oxide is a very caustic
chemical and should be handled with care. As drying agent it is even better than
calcium chloride. While absorbing water, it does not liquefy. Impure calcium
oxide can be obtained as cement in hardware stores.
![]() Calcium sulfate hemihydrate or anhydrous is a white powder, which slowly reacts
with water. It is called gypsum. When this is mixed with water, then another
hydrate is formed, possibly up to the dihyrate. During this process it hardens.
It is used for construction purposes and can be purchased at hardware stores.
For the home lab, it is not really interesting. It might be interesting for
certain pyrotechnic purposes, for the same reason as calcium carbonate might be.
Calcium sulfate hemihydrate or anhydrous is a white powder, which slowly reacts
with water. It is called gypsum. When this is mixed with water, then another
hydrate is formed, possibly up to the dihyrate. During this process it hardens.
It is used for construction purposes and can be purchased at hardware stores.
For the home lab, it is not really interesting. It might be interesting for
certain pyrotechnic purposes, for the same reason as calcium carbonate might be.